PET and MRI Radiomic Features Can Help Personalize Breast Cancer Diagnosis & Treatment
Radiomics is an emerging discipline in radiology. It is the process of extracting quantitative image features from multiple imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and converting them into mineable data for other omics-like analysis.
In cancer management, these multiple imaging modalities are often prescribed for tumor detection, staging and characterization. They also provide rich collective data that can be used for further in-depth analysis. While radiomic features from anatomical images, such as CT, have shown significant potential in predicting survival outcome, and in associating with clinical and genomic features of various cancers, there are few studies investigating radiomic features derived from molecular imaging modalities such as PET/CT and even fewer studies of radiomics for the same disease across imaging modalities such as PET and MRI.
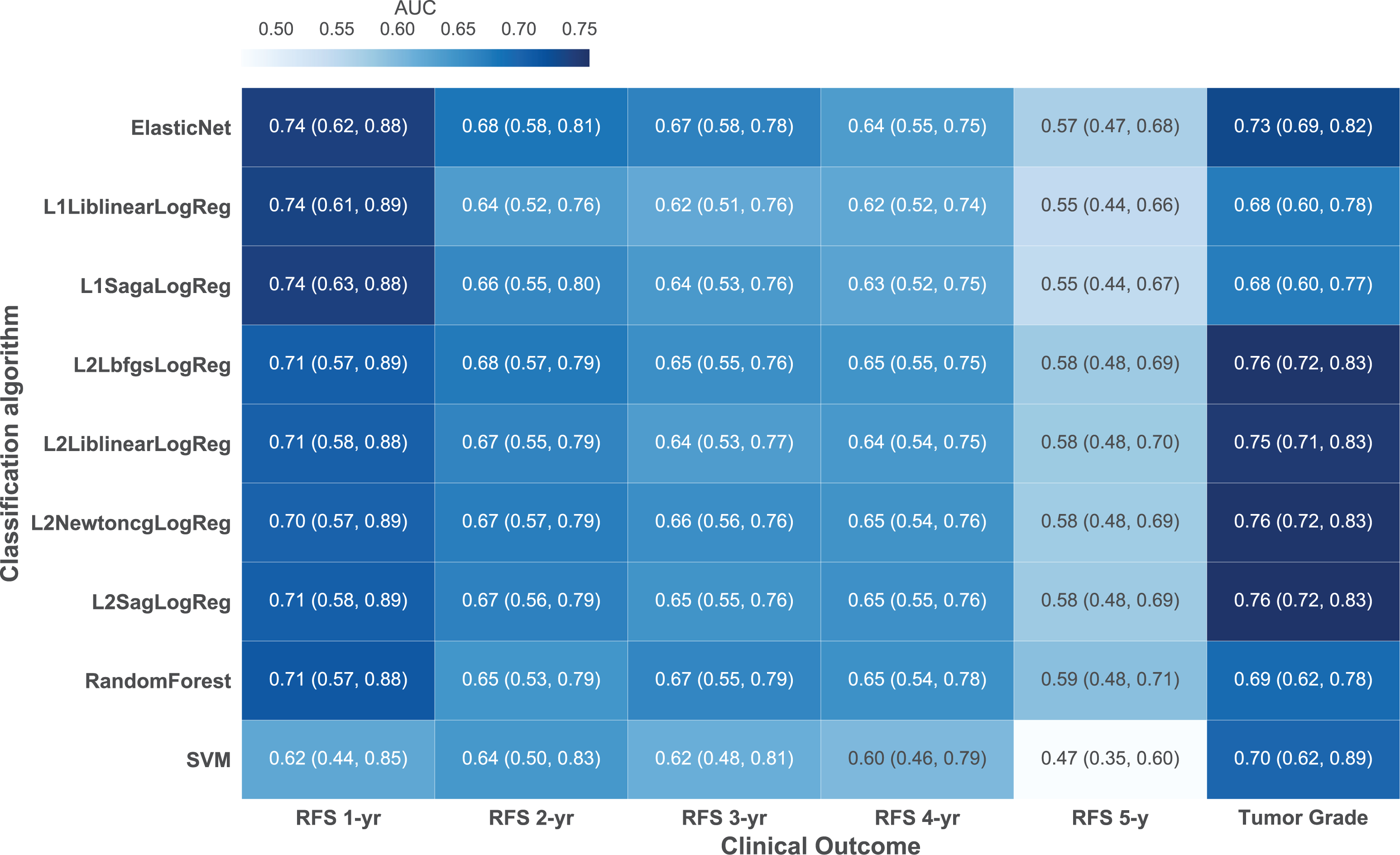
Researchers with the UC San Francisco Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging set out to determine the benefit of using multi-modality radiomics data from PET and MR images in the characterization of breast cancer phenotype and prognosis. To perform the research, 84 features were extracted from PET and MR images of 113 breast cancer patients. They carefully investigated the association of higher-order image features from PET and MRI with breast cancer phenotypes and prognosis. They concluded that radiomic features from PET and MR images could be helpful in deciphering breast cancer phenotypes and may have potential as imaging biomarkers for prediction of breast cancer recurrence-free survival.
Their research was recently published in npj Breast Cancer, part of the Nature Partner Journals series, dedicated to publishing the finest research on breast cancer research and treatment. Youngho Seo, PhD, professor in residence and director of nuclear imaging physics was a senior author on this study. Fellow authors from UCSF include Laura Esserman, MD, MBA; Elissa Price, MD; Nola Hylton, PhD; Spencer Behr, MD; Ella Jones, PhD; John Kornak, PhD; Vignesh Arasu, MD; Timothy Copeland, MPP; Roy Harnish, MS; Ben Franc, MD, and Shih-ying Huang, PhD.
