Intravenous Administration of Contrast Agents for Enhanced CT or MR Scans in Adults
- Peripheral IVs
- PICCS (peripherally inserted central catheters)
- Chest Ports
- Central Lines
- Dialysis catheters should not be used to administer contrast agents
- IV cannulas inserted into the Internal or External Jugular Vein
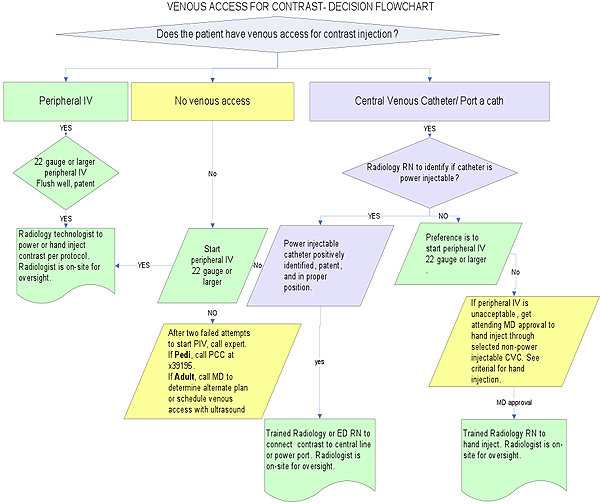
Safe intravenous access, for the injection of intravenous contrast, is vital in obtaining high quality contrast enhanced or angiographic studies. Proper technique is used to avoid the potentially serious complications of contrast media extravasation and/or air embolism. When the proper technique is used, contrast medium can safely be administered intravenously by power injector, at high-flow rates of up to 5 mls/second. A short peripheral IV catheter in the antecubital or forearm area is the preferred route for contrast administration. However other routes may need to be used and each is considered separately below. The follow flowchart will assist in the decision of obtaining proper venous access for contrast administration.
 Click on image to view larger.
Click on image to view larger.
1) Peripheral IV
Doctors, nurses and Radiology technologists can insert peripheral IV catheters in the adult arm for the purpose of contrast administration. A peripheral intravenous line (20 gauge) in the antecubital or forearm area is preferred when power injections are needed in adults. Although 22-gauge catheters may be able to tolerate flow rates up to 5 ml/sec, the 20-gauge or larger catheter is preferable for flow rates of 3 ml/sec or higher. When a 22-gauge catheter is used, the technologist should adjust the injection rate to < 3.0 cc/sec in adults (2.0 cc/sec. in pediatrics) to suit the smaller bore catheter.
A small peripheral line IV of 24 gauge, may only be used for contrast by hand injection.
Before initiating the injection, the position of the catheter tip should be checked for venous backflow by withdrawing blood and flushing with normal saline. A saline test flush may be used to test the power injection. Standard procedures should be used to clear the syringe and pressure tubing of air before connecting to the catheter. A critical step in preventing significant extravasation is direct monitoring of the venipuncture site by palpation during the initial portion of the contrast medium injection. If no problem is encountered during the initial injection, the individual monitoring the injection exits the CT scan room before the scanning begins. If extravasation is detected, the injection is stopped immediately. If the patient complains of pain the injection should be stopped and the patient examined for signs of extravasation.
2) PICCs (peripherally inserted central catheters)
PICCs that are power injectable are clearly marked "power injectable" and have a maximum flow rate printed on the catheter lumen or hub itself. They can be power injected by a trained radiologic technologist, MD or RN. and should only be be used according to manufacturer's guidelines in the presence of appropriately trained personnel. These lines include, but are not limited to the following:
- The PowerPICC line by BARD Access Systems. The Power PICC is a purple central venous catheter that has been approved by the FDA for power injection of contrast in adults and children. Refer to the marking on the hub of the catheter to determine the maximum rate of injection and to choose the correct lumen for power injection. Power PICCs of 4Fr single lumen, 5Fr single or double lumen and 6Fr single or double lumen can be power injected at 5 mls/sec and a maximum power injector pressure setting of 300 psi.

- Cook Spectrum PICC. The line with the red hub should be used for power injection. All catheter tube extensions are labeled with port name, gauge, and flush volume. A 4Fr single lumen can be injected at 4mls/see, a 5Fr single lumen at 7 mls/sec and a double lumen at 5 mls/sec at a Maximum Injector Pressure limit of 325 psi.

- The Navilyst Power injectable PICC has the max ml/sec marked on the clamp on the lumen of the power injectable lumen. Depending on the lumen of the catheter the rate ranges from 3.5 mls/sec to 5 mls/sec at a Maximum Power Injector pressure of 300 psi. It has a clear extension tubing to visualize the blood return. Patients may come with this PICC line placed at an outside hospital.
- Morpheus Smart PICC by AngioDynamics has the max ml/sec marked on the clamp on the lumen of the power injectable lumen, which is usually 5 mls/sec. A patient may come with this PICC line placed at an outside hospital.
3) Chest Ports
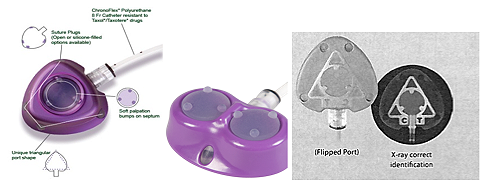
- The Smart Port by AngioDynamics is a subcutaneous indwelling central venous access port that is FDA-approved for power injection of contrast. It has distinctive scalloped edges that can be palpated or seen on a CXR or scout view. Note the “CT” is visible on x-ray image of the newer models of ports as an identifier that this port is power injectable. It is indicated for power injection of contrast media up to 5 mL/sec. and 300 psi pressure limit setting, when used with a Gripper Plus Huber needle. They are MRI conditional at 3 Tesla. This is the most common adult chest port currently placed at UCSF.

- Smith Medical has power P.A.C. port that is power injectable up to 5 ml/sec. when used with a Gripper Plus power P.A.C. Huber needle. They are MRI conditional at 3 Tesla. There are single-lumen and dual-lumen ports that are power injectable. Note that the word “CT” is visible on a x-ray image of the newer models of ports as an identifier that this port is power injectable.
- The PowerPort by BARD is a subcutaneous indwelling central venous access port that is FDA-approved for power injection of contrast. It has a distinctive triangular shape that can be palpated (three palpable “bumps” arranged in a triangle) or seen on a CXR or scout view (either an opaque rounded triangle or a triangular outline with the letters “CT” under the triangle). It is indicated for power injection of contrast media up to 5 mL/sec and a 300 psi pressure limit setting, when used with a Gripper Plus Huber needle. There are also dual-lumen PowerPorts by BARD.
4) Central Lines
- The ARROWgard Blue plus pressure injectable CVC is pressure injectable for CT scanning for up to 10 mL/sec. The center lumen is marked with the max ml/sec on the hub of the catheter. The words “No CT” are marked on the lumen that is not to be used for power injection.

- Power Hickman catheter by BARD is a tunneled central venous catheter that can be injected up to maximum flow rate of 5 mL/sec. and 300 psi pressure limits setting.

- Power Hohn by BARD comes in single, double, and triple lumen catheters. The specific lumen is marked if it is power injectable, up to a maximum of 5 mL/sec at a maximum of 300 psi.

Criteria to POWER INJECT through a power injectable CVC
- The CVC must be verified as compatible for power injection (see above).
- A trained Radiology RN/MD, or Radiologic technologist will help the imaging technologist connect the power injectable CVC to the power injector when the following conditions are met.
- The 5 rights for medication administration are satisfied. Check patient identification to ensure the Right Patient, check the Right Contrast (medication), check the Right Dose, check the Right Route, and check the Right Time.
- Do a visual inspection of the external portion of the catheter for integrity and proper position.
- Check that the catheter flushes properly with normal saline and withdraws properly.
- The technologist will perform the power injection after the power injector has been connected to the power injector catheter.
- The maximum flow rate and psi for adult injection is 5 mL/sec at <300 psi, and the maximum flow rate and psi for Pediatric is 2 mL/sec at <300 psi. The injection rate will be dependent on the specific catheter type, size, and specific exam protocol.
Criteria to HAND INJECT through a power injectable CVC
The Radiology nurse will determine the catheter type and size by visual inspection and review of documentation. Hand injection of contrast is acceptable only if the examination does not require arterial phase of injection (CTA). Adult patients with non-power injectable central line, may undergo contrast injection for a CT/MRI by hand injection into the CVC, except into dialysis catheters.
A trained Radiology RN/MD will perform the hand injection into the non-power injectable CVC per protocol followed by 10 mL 0.9 sodium chloride flush when the following conditions are met.
- The 5 rights for medication administration are satisfied. Check patient identification to ensure the Right Patient, check the Right Contrast (medication), check the Right Dose, check the Right Route, and check the Right Time.
- Do a visual inspection of the external portion of the catheter for integrity and proper position.
- Check that the catheter flushes properly with normal saline and withdraws properly.
5) Dialysis catheters
Dialysis catheters are NOT to be used, with the exception of the BARD Trialysis catheter as described below. Dialysis or apheresis catheters should never be accessed without the explicit approval of the responsible attending or fellow in Nephrology or Hematology/Oncology.
- BARD Trialysis catheter has a power injectable third lumen. Only this lumen may be used for contrast administration. The maximum flow rate is marked on this purple lumen.
6) IV cannulas inserted into the Internal or External Jugular Vein
Short IV cannulas placed in the jugular vein should not be power injected by the technologist or RN because of the dangers of extravasation in the neck. The preference is to attempt a peripheral IV in the patient for contrast administration. If this is not possible and it is deemed necessary for the patient to receive a contrast scan, then contact the Radiologist. The line will be checked for blood return and flushed with saline bolus. It can be hand injected by a Radiology RN or MD for contrast enhanced scan but not for a CT angiogram.